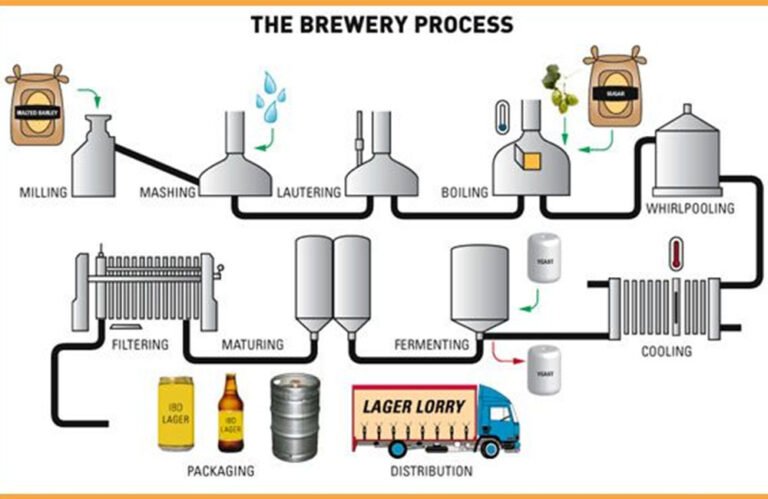
Orthopedic
Orthopedic care plays a vital role in how we move, work, rest, and live our everyday lives. From walking and lifting to typing and stretching, nearly every physical action depends on healthy bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, and tendons. The field of orthopedic medicine exists to protect, repair, and improve this complex system that keeps the human body mobile and strong.
Today, orthopedic knowledge goes far beyond broken bones and casts. It covers sports injuries, chronic joint pain, posture problems, age-related degeneration, advanced surgeries, rehabilitation, and preventive care. As lifestyles become more active—and sometimes more sedentary—the importance of orthopedic awareness continues to grow.
This in-depth article explores orthopedic care from every angle. Written in a casual yet expert tone, it is designed to be easy to read, medically accurate, and highly informative. Whether you are a student, patient, fitness enthusiast, or simply curious, this guide will help you understand orthopedic health clearly and confidently.
What Does Orthopedic Mean in Modern Healthcare?
The term orthopedic refers to the branch of medicine focused on the musculoskeletal system. This includes bones, joints, muscles, ligaments, tendons, nerves, and connective tissues that support movement and stability. Orthopedic care ensures that this system functions smoothly and efficiently.
In modern healthcare, orthopedic treatment is both preventive and corrective. It addresses sudden injuries like fractures and dislocations, as well as long-term conditions such as arthritis, spinal issues, and joint degeneration. The goal is not only to heal damage but also to restore quality of life.
Orthopedic medicine has evolved significantly over time. What once relied mainly on immobilization and surgery now includes advanced imaging, minimally invasive techniques, personalized rehabilitation, and lifestyle-focused prevention strategies. This evolution has made orthopedic care more effective and patient-centered than ever before.
The Importance of Orthopedic Health in Everyday Life
Orthopedic health affects people of all ages, from children learning to walk to older adults maintaining independence. Healthy bones and joints allow individuals to stay active, productive, and pain-free. When orthopedic health is compromised, even simple tasks can become challenging.
Poor orthopedic health often develops quietly. Minor aches, stiffness, or posture problems may seem harmless at first but can lead to serious issues if ignored. Orthopedic awareness helps people recognize early warning signs and take action before problems worsen.
Maintaining orthopedic health also supports mental well-being. Chronic pain and mobility limitations can affect mood, confidence, and social interaction. By addressing orthopedic concerns early, individuals can protect both physical and emotional health.
The Musculoskeletal System and How It Works
The musculoskeletal system is a complex network designed for strength, flexibility, and coordination. Bones form the framework of the body, providing structure and protection for vital organs. Joints connect bones and allow controlled movement.
Muscles generate force and motion, while tendons connect muscles to bones. Ligaments stabilize joints by connecting bones to each other. Nerves transmit signals that coordinate movement and balance. Each component plays a critical role in overall orthopedic function.
When one part of the system is injured or weakened, other parts often compensate, which can lead to further strain. Orthopedic care focuses on restoring balance across the entire system, not just treating isolated symptoms.
Common Orthopedic Conditions You Should Know About
Orthopedic conditions range from mild to severe and can affect any part of the body. Some develop suddenly due to injury, while others progress gradually over time. Understanding common conditions helps people seek appropriate care early.
Arthritis is one of the most widespread orthopedic conditions. It causes joint inflammation, stiffness, and pain, often worsening with age. Back pain and spinal disorders are also common, especially among people with sedentary lifestyles or physically demanding jobs.
Other frequent orthopedic issues include tendonitis, bursitis, fractures, dislocations, and repetitive strain injuries. Each condition requires a specific approach, highlighting the importance of accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.
Orthopedic Injuries and Their Causes
Orthopedic injuries can occur due to accidents, sports, workplace strain, or everyday activities. Slips, falls, and sudden impacts are common causes of fractures and joint injuries. Athletes often experience ligament tears, muscle strains, and overuse injuries.
Repetitive movements are another major cause. Typing, lifting, running, or standing for long periods can gradually stress muscles and joints. Over time, this can lead to chronic orthopedic problems if proper care is not taken.
Age-related changes also contribute to orthopedic injuries. As bones lose density and muscles weaken, the risk of injury increases. Orthopedic prevention focuses on strengthening, flexibility, and balance to reduce these risks.
Orthopedic Diagnosis and Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis is the foundation of effective orthopedic care. Orthopedic evaluation typically begins with a detailed medical history and physical examination. This helps identify symptoms, movement limitations, and possible causes.
Imaging tools such as X-rays, MRI scans, and CT scans provide detailed views of bones and soft tissues. These technologies allow orthopedic specialists to detect fractures, cartilage damage, ligament tears, and structural abnormalities.
Advanced diagnostic methods also include motion analysis and nerve studies. By combining clinical expertise with modern technology, orthopedic professionals can develop precise and effective treatment plans.
Non-Surgical Orthopedic Treatments
Not all orthopedic conditions require surgery. In fact, many issues can be managed successfully with non-surgical treatments. These approaches focus on reducing pain, improving function, and supporting natural healing.
Physical therapy is a cornerstone of non-surgical orthopedic care. It strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and restores movement patterns. Medications, braces, and supportive devices may also be used to manage symptoms.
Lifestyle changes play a significant role as well. Weight management, posture correction, and activity modification can dramatically reduce strain on joints and muscles. Non-surgical care empowers patients to actively participate in their recovery.
Orthopedic Surgery: When and Why It’s Needed
Orthopedic surgery is considered when conservative treatments fail or when damage is severe. Surgical intervention aims to repair, replace, or reconstruct affected structures to restore function and reduce pain.
Common orthopedic surgeries include joint replacements, fracture repairs, ligament reconstructions, and spinal procedures. Advances in surgical techniques have made these procedures safer and more precise.
Minimally invasive surgery is now widely used in orthopedics. Smaller incisions, improved instruments, and faster recovery times have transformed patient experiences. Surgery is no longer just about fixing problems—it’s about improving long-term outcomes.
Joint Replacement and Modern Orthopedic Advances
Joint replacement is one of the most significant achievements in orthopedic medicine. It involves replacing damaged joints, such as hips or knees, with artificial components designed to mimic natural movement.
These procedures are often life-changing for individuals with severe arthritis or joint damage. Pain relief, improved mobility, and enhanced quality of life are common outcomes when recovery is managed properly.
Modern materials and surgical techniques continue to improve joint replacement longevity and performance. Orthopedic research focuses on making replacements more durable, natural-feeling, and personalized for each patient.
Sports Orthopedic Care and Athletic Performance
Sports orthopedics focuses on preventing, diagnosing, and treating injuries related to physical activity. Athletes place high demands on their musculoskeletal systems, making specialized care essential.
Common sports-related orthopedic injuries include ligament tears, muscle strains, stress fractures, and joint instability. Proper conditioning, training techniques, and recovery strategies help reduce these risks.
Orthopedic care for athletes emphasizes quick recovery without compromising long-term health. Rehabilitation programs are tailored to restore strength, coordination, and confidence while minimizing the chance of re-injury.
Pediatric Orthopedic Considerations
Children have unique orthopedic needs because their bodies are still growing. Pediatric orthopedics addresses developmental issues, congenital conditions, and childhood injuries.
Growth plates are particularly important in children. Injuries to these areas require careful management to avoid long-term complications. Early diagnosis and treatment support healthy growth and alignment.
Pediatric orthopedic care also focuses on posture, gait, and activity habits. Encouraging proper movement patterns early helps prevent future orthopedic problems and promotes lifelong musculoskeletal health.
Orthopedic Care for Aging Populations
As people age, orthopedic care becomes increasingly important. Natural changes in bone density, muscle strength, and joint flexibility can affect mobility and independence.
Conditions such as osteoporosis, arthritis, and spinal degeneration are more common in older adults. Orthopedic management aims to reduce pain, maintain function, and prevent falls.
Gentle exercise, supportive therapies, and preventive strategies are key components of orthopedic care for aging populations. The goal is to support active, confident living at every stage of life.
The Role of Rehabilitation in Orthopedic Recovery
Rehabilitation is a critical phase of orthopedic care. Whether following injury or surgery, rehabilitation helps restore strength, movement, and confidence.
Physical therapy programs are designed to progress gradually, allowing tissues to heal while rebuilding function. Consistency and patience are essential for successful outcomes.
Rehabilitation also educates patients about body mechanics and injury prevention. This knowledge empowers individuals to protect their orthopedic health long after formal treatment ends.
Orthopedic Prevention and Long-Term Wellness
Preventive orthopedic care focuses on maintaining strength, flexibility, and balance. Regular physical activity, proper nutrition, and ergonomic habits all support musculoskeletal health.
Simple practices such as stretching, proper lifting techniques, and posture awareness can prevent many common orthopedic issues. Prevention reduces the need for medical intervention and improves overall well-being.
Long-term orthopedic wellness is about consistency. Small daily choices accumulate over time, shaping how the body functions and feels. Prevention is one of the most powerful tools in orthopedic health.
Technology and Innovation in Orthopedic Medicine
Technology continues to reshape orthopedic care. Advanced imaging, robotic-assisted surgery, and data-driven rehabilitation tools enhance precision and outcomes.
Wearable devices now track movement patterns and recovery progress. These tools help orthopedic professionals personalize treatment and monitor improvement in real time.
Innovation in materials science also supports orthopedic advancement. Stronger implants, biologic therapies, and tissue engineering are expanding what orthopedic medicine can achieve.
Choosing the Right Orthopedic Care Approach
Every orthopedic condition is unique. Choosing the right approach involves understanding symptoms, goals, and lifestyle factors.
Collaboration between patients and healthcare providers is essential. Open communication ensures that treatment plans align with individual needs and expectations.
Informed decision-making leads to better outcomes. Understanding orthopedic options empowers individuals to take an active role in their health journey.
Final Thoughts on Orthopedic Health
Orthopedic care is about more than bones and joints—it’s about movement, independence, and quality of life. Healthy orthopedic function allows people to live fully and confidently.
By understanding orthopedic principles, recognizing early signs of trouble, and embracing preventive care, individuals can protect their musculoskeletal health for years to come.
Orthopedic medicine continues to evolve, offering new solutions and hope for people of all ages. Staying informed is the first step toward stronger movement and better living.